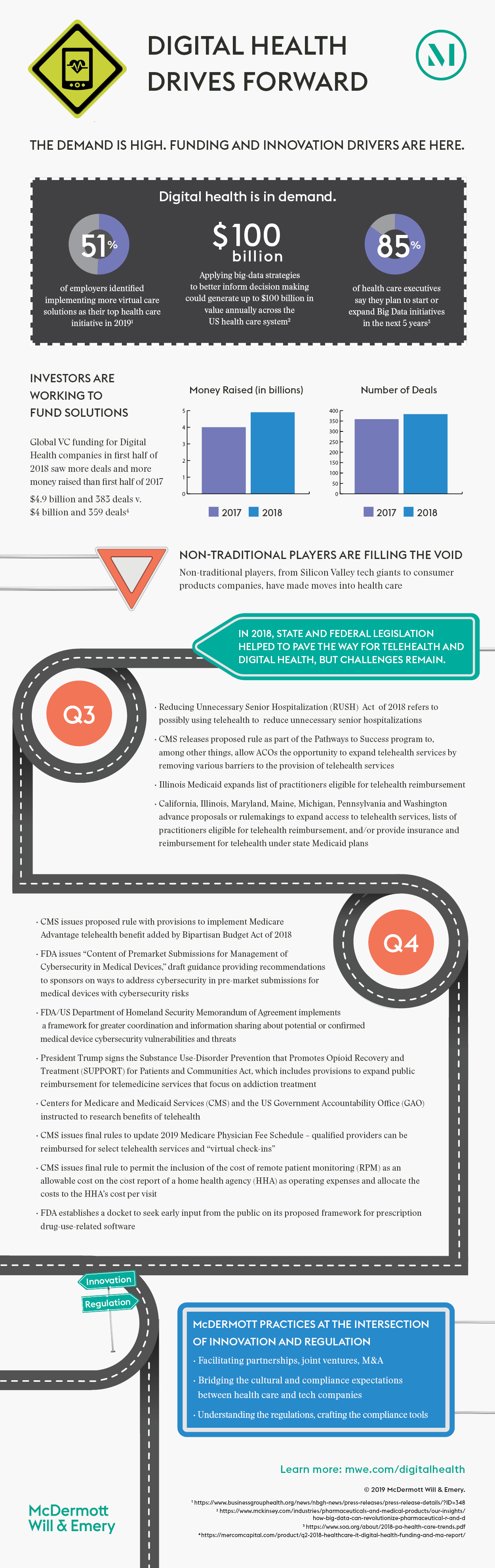
New digital health regulations arose at the federal and state level in 2018, bolstering the existing legal framework to further support and encourage digital health adoption in the context of care coordination and the move to value-based payment. McDermott’s 2018 Digital Health Year in Review: Focus on Care Coordination and Reimbursement report – the second in a four-part series – highlighted these developments within the digital health landscape. These efforts brought changes to coverage of telehealth and other virtual care services, as well as information gathering for regulatory reform, and can help bridge the gap between research, funding and implementation as regulations build a framework within which companies can deploy their products, receive reimbursement and demonstrate value to patients. Here we outline digital health developments from the second half of 2018 and how they can help drive digital health forward in 2019. For a closer look at key care coordination and reimbursement developments that shaped digital health in 2018, along with planning considerations and predictions for the digital health frontier in the year ahead, download our full report.
To view the first report in the series, 2018 Digital Health Year in Review: Focus on Data, click here.
read more


 Subscribe
Subscribe